Dysbacteriosis is a violation of the microbial balance on the human body or inside it. Not all modern experts recognize dysbacteriosis as an independent disease. Most often it is called a disorder, a bacterial imbalance that is easily amenable to medical correction. This pathological condition is a change in the ratio of favorable and opportunistic bacteria. In the field of gastroenterology, intestinal dysbiosis is often encountered, but in some cases, an imbalance of microorganisms can develop in the reproductive organs, on the skin and in the oral cavity.
What is the intestinal microflora
Every adult has billions of microorganisms in their intestinal tract, the total mass of which can reach three kilograms. This is about half a thousand varieties of bacteria settled in almost all parts of the intestine.
A logical question arises - what are these bacteria for? The purpose of microorganisms is to digest the food that enters the body. Microbes are actively involved in the synthesis of nutrients and remove toxins. In humans, mainly aerobic lactobacilli and anaerobic bifidobacteria live in the intestine.
All "inhabitants" of the intestinal tract are conditionally divided into three categories:
Useful bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. They are the majority, so these microorganisms maintain the balance of other microbes, restraining the growth of pathogenic microbiota. With a decrease in the number of bifido- and lactobacilli, the immune system weakens, and a tendency to allergic reactions appears.
The second group of representatives of the intestinal microflora are neutral microorganisms. They are localized in specific places, do not bring any tangible benefits or harm.
Conditionally pathogenic microbes are present in the intestines of every healthy person, but if the immune system fails, these bacteria begin to multiply actively, which becomes a favorable background for the development of a whole list of diseases. Conditionally pathogenic consider staphylococci, streptococci, fungi of the genus Candida.
Causes
The number of representatives of each species is regulated by the laws of natural biological selection: for those who have multiplied strongly, there is not enough food, and the weakest die, or their “cohabitants” create unfavorable conditions for their existence. The cause of dysbacteriosis is a change in the normal balance - the number of bifidobacteria and lactobacilli is reduced, and pathogenic microbes, on the contrary, actively multiply. In this context, factors that can suppress healthy microflora should be considered.
These are considered:
Long-term use of potent drugs. Most often, the problem manifests itself after antibiotics. Intestinal dysbacteriosis can also develop against the background of regular use of laxatives, antidepressants, immunosuppressants, steroids and other medications.
Unbalanced diet, lack of vital vitamins in the body. The state of the gastrointestinal tract is dramatically affected by addiction to chemical food additives (preservatives, dyes, flavors, stabilizers, etc.). Not very well on the intestinal flora may be affected by a sudden change in diet and style.
Chronic diseases of the digestive system, including gastric ulcer, cirrhosis of the liver, inflammation of the pancreas, chronic cholecystitis, Crohn's disease.
Worm infestations - helminths secrete poisonous substances that are deadly for beneficial microorganisms.
The cause of dysbacteriosis can be recent operations on the intestines, psycho-emotional shocks, neurological pathologies. Sometimes completely healthy people can suffer from this pathological condition. Then the cause is sought in the specifics of professional activity, seasonal changes in nutrition.
Stages of development of dysbacteriosis
The process of replacing beneficial bacteria with pathogenic ones takes some time, so experts have identified the main stages in the formation of an imbalance in the intestines. At the beginning of the development of dysbiosis, the number of lacto- and bifidobacteria decreases. Further, conditionally pathogenic microorganisms are activated - they, having lost their main competitors, populate the free intestinal lumens.
Scientists have found that some bacteria multiply very quickly, while others increase their numbers at a slow pace, becoming active only at advanced stages of dysbacteriosis. Even minor chemical and biological disturbances are sufficient to change the composition of the microbiota.
Taking into account changes in the quantitative and qualitative composition of the microbial flora, several stages of dysbiosis are distinguished. At the same time, there are no clear distinctions in terms of symptoms:
Initial. At this stage, the number of lacto- and bifidobacteria is reduced, which in a healthy body inhibit the activity of other microorganisms. It is quite difficult to single out the dominant representatives of the intestinal flora. At this stage, the disease is latent.
Second. The numerical advantage is established for colibacteria. Most of these microbes have atypical enzyme activity, which is detected during laboratory tests.
Third. At this stage of the disease, in patients who have undergone a complex of clinical studies, a mixed population of the intestine is detected, where mainly opportunistic bacteria predominate.
Complicated. If the analyzes show an excessive presence of Proteus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, we can talk about the onset of the fourth stage of dysbacteriosis. An advanced form of dysbiosis is diagnosed in patients who completely ignore the need for treatment.
In some cases, a person's well-being worsens as the pathology progresses. Unhelpful microbes colonizing the intestines practically cannot cope with the functions that lacto- and bifidobacteria performed.
Classification of intestinal dysbiosis
Dysbiosis can occur in the large and small intestines. Colon pathology is more common among patients. With dysbacteriosis of this type, the microflora is disturbed in the stomach, and in the duodenum, and in the intestines. Pathology can acquire a long course, manifesting itself with periodic exacerbations and negatively affecting the patient's habitual lifestyle.
In the small intestine, dysbiosis develops with excessive colonization of the walls. Patients with this form of microflora disturbance constantly feel a dull background pain in the navel.
Another classification of intestinal disorders is distinguished by the nature of the course and the severity of symptoms. According to her, there is mild, moderate and severe dysbacteriosis. This is a violation of the microflora that appears in perfectly healthy people or may occur as a secondary manifestation of another disease.
In the first case, intestinal dysbiosis is divided into:
professional;
age (in the elderly);
nutritional (caused by eating junk food);
seasonal.
Dysbacteriosis occurs in an acute, protracted or chronic form with a typical clinical picture or without any symptoms. Treatment of intestinal dysbacteriosis in adults is undesirable to carry out independently, without prior examination and consultation with a doctor. The choice of therapeutic tactics in violation of the microflora is determined by the peculiarity of the course of the pathology and the stage of the disease.
How the disease manifests itself: patient reviews
The characteristic symptoms of a change in the bacterial balance in the intestinal region are:
Chair disorders. Judging by the reviews, with dysbacteriosis, patients are more likely to suffer from diarrhea than from constipation. In older people, on the contrary, constipation develops due to reduced intestinal peristalsis.
Changes in the composition, shape and color of feces. Their cause is the actively ongoing processes of decay and fermentation in the intestines. Turning to the doctor, patients note that the feces become watery, frothy, lose their dark pigment, emit a specific sour or putrid odor.
Burning and itching in the anus. Liquid dysbiosis feces cause redness and irritation of the anus.
Flatulence. Increased gas formation becomes a frequent symptom of intestinal dysbacteriosis in adults and children. The gases may be offensive or odorless, emitted with or without sound.
Bloating. Often, this symptom worries patients in the evening or after eating certain foods (cabbage (fresh or sour), tomatoes, cucumbers, muffins, apples, etc.).
Nausea, occasional vomiting. As a result of impaired digestion, other signs of dysbiosis may appear - loss of appetite, rotten taste in the mouth, weight loss, weakness.
People with a violation of the intestinal microflora are not able to fully empty the intestines. At the same time, not all of these signs of dysbacteriosis must necessarily be observed in a patient. Basically, patients complain of constipation or loose stools, as the food is first broken down by microorganisms, and then absorbed into the blood. Without the help of intestinal bacteria, the body is not able to fully absorb nutrients, so the lack of intestinal "inhabitants" causes nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
With dysbacteriosis, the likelihood of the appearance of other symptoms is not excluded, but it would be more correct to refer them not to the manifestations of the disease, but to the consequences and complications. For example, hypovitaminosis or beriberi develops against the background of non-absorption in the body of nutrients that enter the intestines.
About diagnostics
An examination for intestinal dysbacteriosis is necessary in order, first of all, to differentiate the pathology from other diseases of the digestive system - colitis, enterocolitis, gastritis. The patient will have to pass more than one analysis for dysbacteriosis. After all, before prescribing the appropriate treatment, the doctor must understand what he has to deal with.
Dysbacteriosis is a condition that cannot be determined without a series of laboratory procedures. The symptoms of this pathology are very similar to the symptoms of other disorders in the body. After collecting the patient's complaints, examination, palpation of the abdomen and taking an anamnesis, the specialist will prescribe several diagnostic procedures. Despite the fact that dysbacteriosis is not assigned a separate code in ICD-10 (violation of the intestinal microflora is not recognized by WHO as an official independent disease), domestic experts diagnose the disease based on the results of the following analyzes and instrumental studies:
Fecal analysis. This is the most specific technique used to assess the condition of the intestine. In the next section of the article, we will dwell on its description in detail.
Clinical blood test. In patients with dysbiosis, blood counts will indicate inflammation or probable bleeding in the intestinal tract, as well as anemia.
ultrasound. It is performed to rule out or confirm other diseases of the abdominal cavity.
X-ray of the intestine. Patients are referred for this procedure if the doctor suspects a neoplasm.
Colonoscopy. The procedure is prescribed mainly only for adult patients for endoscopic examination of the large intestine.
Fecal analyzes
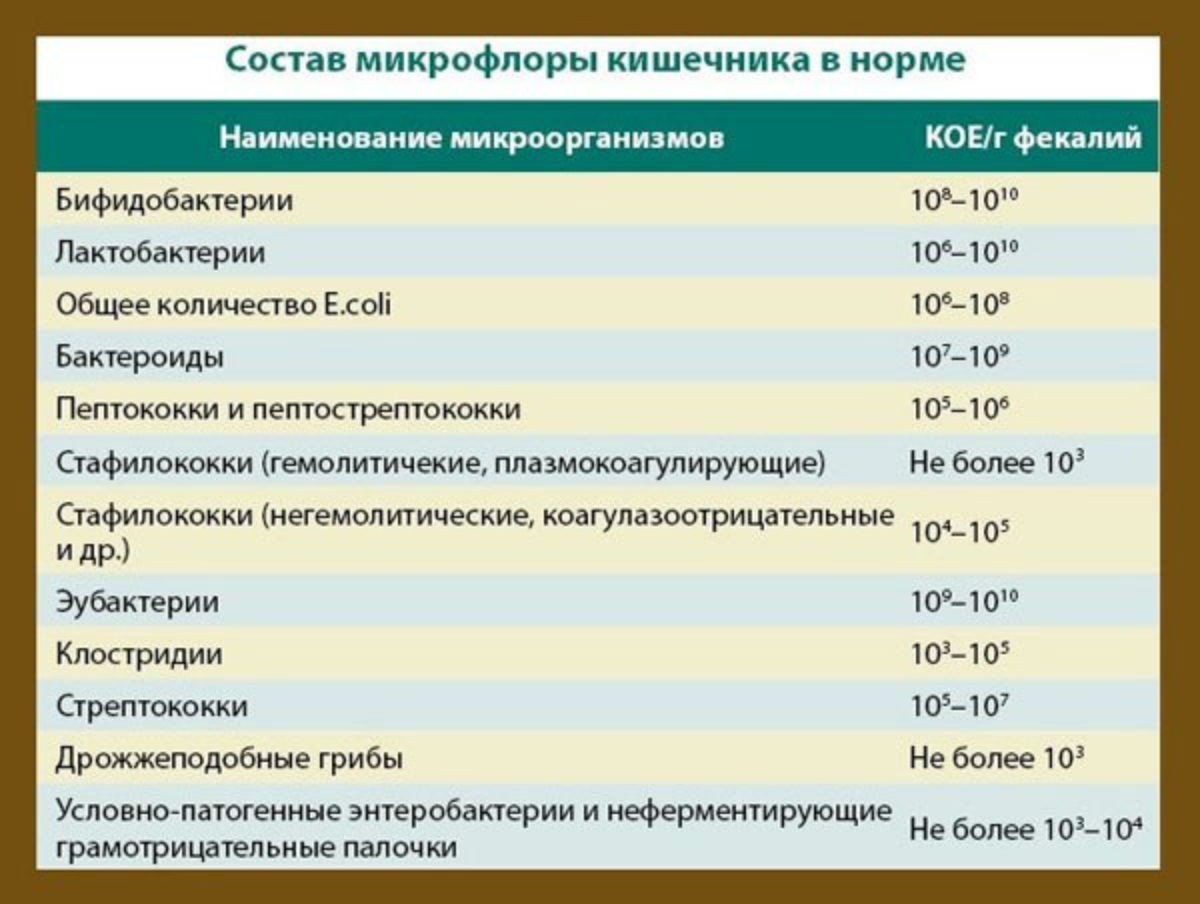
The purpose of this study is to establish the exact qualitative and quantitative composition of bacteria in the intestine. It is recommended to pass feces for dysbacteriosis with persistent stool disorders, prolonged nausea and other disorders of the digestive system. Today, doctors prescribe the following laboratory tests of stool:
Coprogram. Its implementation is especially important for prolonged antibiotic therapy of diseases of the upper respiratory tract, joints, and infections. The coprogram allows you to get a physical description of the contents of the intestine, evaluate its color, shape, smell, determine the presence of purulent, mucous and bloody impurities, the remains of undigested food, and also establish the microscopic content of fiber, fats, salts, starches and other substances in the feces.
Bakposev. A bacteriological study on a nutrient medium provides detailed information on the number of microbes per 1 g of excrement (CFU / g - unit of measurement). It takes more time to detect dysbacteriosis in the feces by conducting bakposev than to perform a coprogram, and therefore this method is not used in all cases.
Biochemical analysis. This is one of the effective and informative ways to carry out express diagnostics, which not only demonstrates microflora disorders, but also determines the intestinal section in which the disorder has occurred.
It is the latter diagnostic method that is most preferable in some cases, since thanks to it it is possible to quickly obtain results and their interpretation. With dysbacteriosis, biochemical analysis of feces accurately determines the concentration of compounds. This method is undemanding to the freshness of the samples submitted for research - yesterday's feces are also suitable for analysis.
Nutrition for violations of microflora
Treatment of dysbacteriosis is not only taking medications. To restore the balance of microbes in the intestines, normal growth and reproduction of beneficial bacteria, dietary fiber, pectin, and amino acids are urgently needed.
You can fill the lack of these substances with the help of food (vegetables, fruits, soy milk, cereals and algae). With a deficiency of lacto- and bifidobacteria, patients are advised to lean on natural fermented milk products. Preference should be given to low-fat kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese without flavorings and flavorings.
Together with food, prebiotics enter our body - these are substances that are not digested in the intestines, but serve as a nutrient medium for living microbes. These include lactulose and oligosaccharides, including inulin, galactose, fructose isomers. All of them are present in sufficient quantities in dairy products and cereals, but wheat, corn, garlic, and onions have the highest concentration of prebiotics.

Prebiotics can also be bought at the pharmacy. What are the most effective for dysbacteriosis? Those containing natural or artificial lactulose, oligosaccharides:
"Duphalac";
"Normaze";
"Prebio";
"Lactusan".
Probiotics
Unlike prebiotics, probiotics are dysbacteriosis preparations containing live bacteria. They are:
Monocomponent - the composition of such probiotics includes microbes of only one type. The most common drugs for dysbacteriosis are Bifidumbacterin, Lactobacterin, Kolibacterin. The course of treatment averages no more than one and a half months.
Symbiotics are probiotics that contain several types of representatives of the obligate flora at once (Bifikol, Bifiform, Lineks). Such drugs for dysbacteriosis are usually taken no longer than two weeks.
Antagonists are drugs that contain living microbes that are not related to the obligate microbiota, but are capable of inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria (Enterol, Bactisubtil, Bactisporin). As a rule, the duration of treatment with antagonists does not exceed one week.
Combined probiotics have a special immunomodulatory property. Among the drugs of this group, there is a high demand in pharmacies for Acipol and Bifiliz.
Combined synbiotics - such drugs for dysbacteriosis successfully combine living representatives of the obligate flora and prebiotics (Bifido-bak, Maltodophilus, Laminolact).
The duration of treatment with synbiotics is at least three weeks.

It is important to understand that probiotics are not intended solely for intestinal colonization. Beneficial bacteria must again compete with the pathogenic flora, thereby suppressing its growth in order to restore the lost balance. However, at the advanced stage of dysbiosis, probiotics alone are not enough. Then antibacterial and antiseptic agents come to the rescue.
Antimicrobials
Antibiotics and antiseptics are practically not absorbed in the intestines and prevent the reproduction of pathogenic flora. At the same time, many doubt the advisability of using antibacterial agents, believing that they only aggravate the already difficult condition of the intestine.
Can dysbacteriosis develop in a healthy person while taking antibiotics? It's no secret that such a probability exists and it is quite high. But the thing is that in the treatment of dysbacteriosis from antibiotics there can be no harm if they are selected taking into account the sensitivity of a particular type of pathogenic microorganisms. Antibiotics have practically no effect on beneficial microflora.
Among the drugs for dysbacteriosis, which are prescribed for both adults and children, it is worth noting:
"Intetrix" - an intestinal antiseptic with quinolones in the composition. Available in the form of capsules and suspensions. The duration of the course of treatment is 3-5 days. For children, the drug is prescribed from the age of 14.
"Nifuroxazide" is a medicine from the group of nitrofurans in the form of a suspension. Analogues of "Nifuroxazide" is "Enterofuril", "Ersefuril".
Antibiotics have a stronger antimicrobial effect and are prescribed only with an established form of dysbiosis. In the case of the predominance of microbes of the staphylococcal species in the microflora, macrolides and penicillins are prescribed, namely Clarithromycin, Oxacillin, Amoxicillin and their analogues. If the analysis of feces for dysbacteriosis shows the presence of proteins or altered forms of Escherichia coli, only Nifuroxazide may be enough to restore normal flora.
In comparison with antibiotics, intestinal antiseptics have fewer contraindications and side effects. To suppress pathogenic enterococci, drugs based on ampicillin, erythromycin and levomycetin are used. With candidiasis dysbacteriosis, antifungal systemic drugs are used - Diflucan, Lamisil, Fluconazole, Amphotericin.
In addition to antibiotics, doctors are increasingly turning to the use of bacteriophages in the treatment of intestinal dysbacteriosis. These are live viruses that can infect a specific type of bacteria (Staphylococcus, Proteus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa). They are often combined with antibiotics and antiseptics. These drugs are available in the form of tablets or enemas.
Symptomatic therapy
For the treatment of hypovitaminosis and replenishment of nutritional deficiencies that have arisen against the background of dysbacteriosis, it is recommended to drink a course of multivitamin preparations. To restore weakened immunity, herbal remedies are used - extracts of propolis, magnolia vine, echinacea, eleutherococcus. With severe symptoms associated with intestinal dysbiosis, appropriate drugs should be used.
For example:
with loose stools - sorbents and antidiarrheals, antispasmodics;
with constipation - laxatives, choleretic drugs, antispasmodics ("No-Shpa", "Duspatalin);
with an allergic reaction - antihistamines ("Tavegil", "Loratadin", "Zodak");
sedative medications.
Medical discussions about whether it is necessary to treat dysbacteriosis after antibiotic therapy or exposure to other factors end with an almost unambiguous conclusion - yes, this condition needs to be treated. Thanks to the existing modern drugs, it is possible to bring the microbial balance back to normal in a short period, and in order to prevent the development of intestinal dysbacteriosis in the future, you need to eat right and use antibiotics wisely.
Dysbacteriosis in women
As mentioned at the beginning of the article, the composition of the microflora can be disturbed not only in the intestines, but also on the human body, in the oral cavity, and in the vagina. In women, this is a very common problem, especially in patients aged 30 to 45 years. Vaginal dysbacteriosis does not apply to a sexually transmitted infectious disease, despite the fact that the symptoms of this pathology may be similar to the manifestations of some sexually transmitted diseases.

Just like in the intestines, lactobacilli live in the vagina in women - their number is the most significant. The volume of microorganisms producing lactic acid reaches 90% of the total microbiota. Along with lactobacilli, bifidobacteria are no less important, the maximum number of which is approximately 9 times less than the previous ones.
The normal microflora that colonizes the vagina performs the main protective function - it protects the lower genital organs from infection by pathogenic microorganisms. In the course of laboratory studies, it was found that lactobacilli are able to block the activity of E. coli, vaginal gardnerella, as well as gonorrhea pathogens and other representatives of unfavorable flora.
There are many reasons for dysbacteriosis in women. Most often, a violation of the vaginal microflora occurs in women with a weakened immune system, hormonal failure. Negatively maintaining the normal bacterial state of the vaginal mucosa is reflected in non-compliance with personal hygiene, as well as taking antibiotics and other medications.
Symptoms of vaginal dysbacteriosis are dense white or yellowish discharge with an unpleasant fishy or putrid odor. In healthy women, the vaginal secret is odorless and consists of translucent mucus.
Before treatment of dysbiosis, the patient must undergo an examination to determine the exact composition of the microflora and its sensitivity to antimicrobial agents. Basically, drugs are prescribed in the form of vaginal suppositories with an antifungal or antibacterial component.
Click " Like» and get the best posts on Facebook!

