There are many bacteria and viruses in the human body. They constitute conditionally pathogenic flora and do no harm. But in the event of a decrease in immunity or under the influence of various factors, they begin to multiply rapidly, causing a number of unpleasant symptoms. These bacteria include, which can lead to serious consequences.
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common and dangerous type of bacteria from the genus Staphylococcus aureus.
The bacterium has a spherical shape and belongs to the genus Staphylococcus. They can remain on the mucous membranes and skin for quite a long time. But not in all cases, pathogenic microorganisms cause the development of certain diseases. In some cases, the person is a carrier. According to the latest data of scientists, there are about 40% of such people.
Carriage, depending on many factors, can be transient or permanent. The bacterium can be found in the intestines, nasal cavity, throat, and on the surface of the genital mucosa. It is this prevalence of bacteria that affects the number of diseases that staphylococcus provokes.
It tolerates even heat and drying well.
The death of bacteria is possible only at +70 degrees. In this case, the duration of exposure to high temperature should be at least 15 minutes. Instant death of Staphylococcus aureus is observed at +150 degrees.
The most common disease that the microorganism causes is food poisoning, which is manifested by severe abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea and a number of other symptoms.Staphylococcus is able to multiply on food products. In large quantities, it can be found in butter creams, meat salads and canned food.
Ways of transmission and causes of development
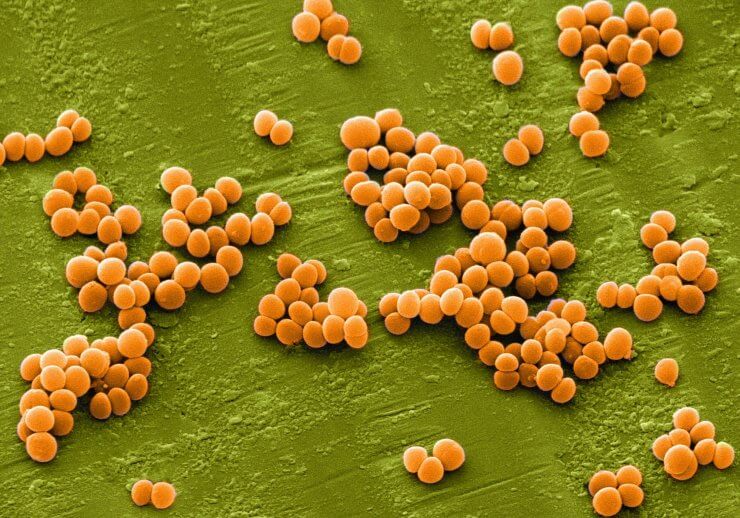
Infection occurs when the infection is transmitted in the following ways:
- Airborne. Possible only in those cases. When bacteria enter the environment along with exhaled air, when they affect the upper respiratory tract or provoke the development of bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Contact household. Infection occurs when using household items on the surface of which the microorganism lives.
- Food. Infection is possible through the use of contaminated products.
- Fecal-oral. The penetration of bacteria into the human body occurs when a person does not wash his hands after going to the toilet. Bacteria contained in feces or vomit, thus get on food and household items.
- Infection is possible when a doctor uses medical instruments when the sterilization rules have been violated.
After entering the body, where the environment is quite favorable for bacteria, microorganisms begin to multiply rapidly, having a negative impact on human health.
More information about Staphylococcus aureus can be found in the video:
But staphylococcus can not always cause the development of diseases. The following factors can provoke the spread of infection:
- Chronic pathologies.
- Reduced immunity against the background of a long illness, regular stress.
- Prolonged contact with a carrier of bacteria.
- Non-compliance with sanitary rules, especially when traveling.
- The presence of wounds, abrasions on the body.
- Eating unwashed vegetables and fruits, low-quality meat and other products.
The main problem in the treatment of staph infection is the viability of the bacterium. They are not affected by cold, dryness or sunlight. Bacteria are able to retain their properties for a long time even in the absence of moisture.
Clinical picture
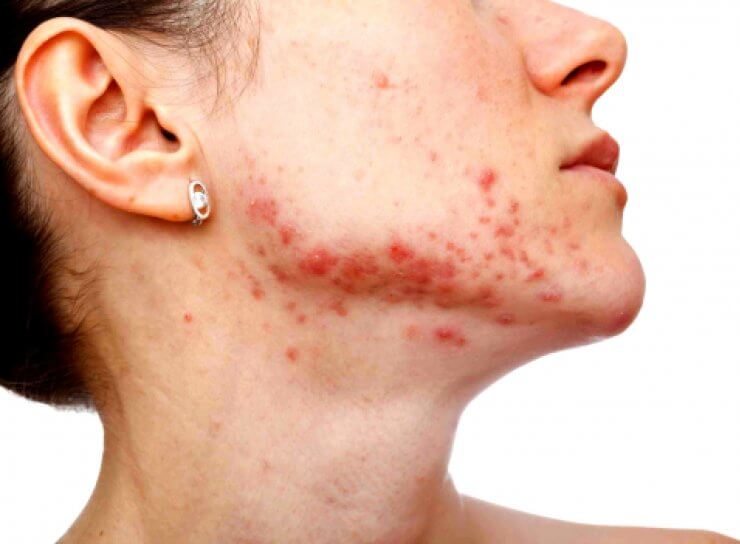
Staphylococcus aureus causes many different diseases. Among them, the most commonly diagnosed are:
- pneumonia
- furunculosis
- eczema
- osteomyelitis
- abscess
- meningitis
- dermatitis
- blepharitis
The clinical picture also depends on the localization of the pathological process. Pathogenic microorganisms can affect many organs and systems:
- GIT. Symptoms appear a few hours after eating low-quality foods. There are repeated vomiting, severe pain in the abdomen, and dry mouth.
- Skin covering. Against the background of the vital activity of bacteria, boils, abscesses, phlegmon or carbuncles can occur. The main signs are a rash on the skin of various types, weakness, lethargy and fever.
- Respiratory system. In adults, respiratory involvement is diagnosed in rare cases. Most often, pneumonia occurs as a result of the activity of microorganisms.
- Mucous. Often, Staphylococcus aureus in adults is found on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and nasopharynx. The inflammatory process causes otitis media and sinusitis. Purulent masses do not always come out and begin to accumulate, which can cause complications.
- Staphylococcus aureus can cause the development of Ritter's disease. Pathology is a manifestation of an infectious lesion, but in exceptional cases it occurs in adults. The main symptoms are a rash that looks like scarlet fever.
The occurrence of severe headache, dizziness, fever, vomiting, heart palpitations and a decrease in blood pressure indicates the occurrence of toxic shock. It manifests itself against the background of a staphylococcal infection.
All clinical manifestations depend on the state of human immunity and the aggressiveness of the pathogen. Treatment depends on the extent and location of the lesion.
Why is Staphylococcus aureus dangerous?

Pathogenic microorganisms do not always cause the development of diseases. But with reduced immunity or the presence of other factors, the spread of staphylococcal infection leads to the development of a number of complications.
Bacteria pose a danger to the human body, due to several factors:
- High resistance to antiseptic solutions. The microorganism withstands boiling for 10 minutes. Its properties are not affected by drying or freezing, it is resistant to ethyl alcohol and hydrogen peroxide.
- A special enzyme that bacteria produce makes them resistant to almost all penicillin drugs.
- The ability to penetrate deep into the body, melting the top layer of the epidermis and sweat glands.
- Bacteria are able to produce endotoxin. It is he who leads to severe poisoning, and in the absence of medical care becomes the cause of severe intoxication of the body.
- One of the serious complications of the disease is bacterial endocarditis. But most often it develops in patients with reduced immunity and people who use drugs.
After treating a disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus, there is a possibility of re-infection, since immunity to bacteria is not developed.
Infection Diagnosis
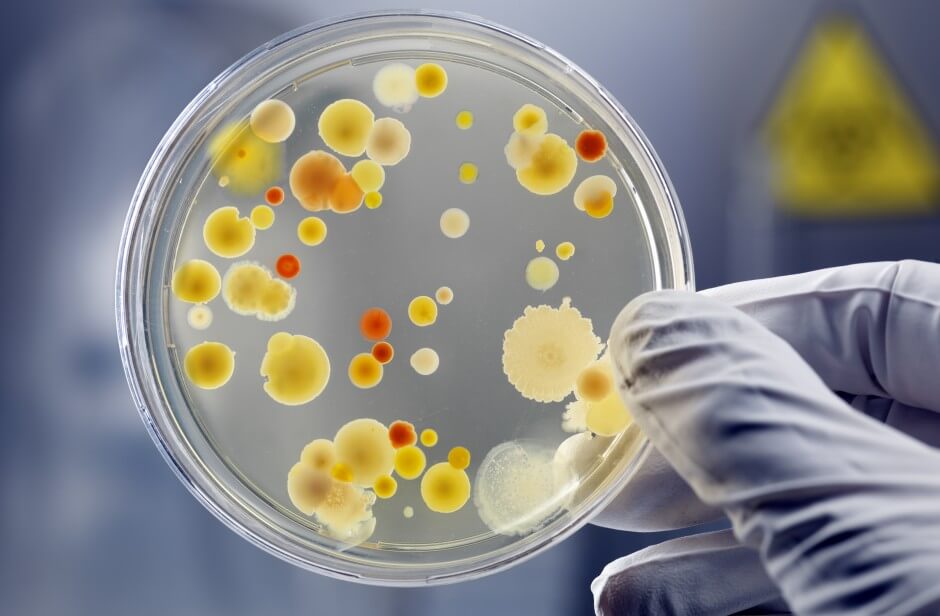
First of all, the specialist conducts differential diagnosis with streptococcal infection. For this, a number of diagnostic measures are assigned:
- Coagulase test in vitro. It lasts for 4 hours, but with a negative result, it is extended for a day.
- Latex agglutination.
- and . It is carried out to establish the level of protein and staphylococci.
- to nutrient media. It is necessary to identify the pathogen and determine its sensitivity to various antibacterial drugs.
- Vidal agglutination reaction. It is carried out to determine the dynamics of therapy. The study is scheduled every 7-10 days.
Sowing is done three hours after the act of defecation. When taking a smear from the mucous membranes, the procedure is carried out only on an empty stomach, before taking all the necessary medications and brushing your teeth.
The results of laboratory tests help the specialist determine the type of staph infection and prescribe the necessary medications.
When diagnosing conjunctivitis, the cause of which was a staphylococcal infection, a smear is prescribed, which is taken from the lower eyelid. To do this, use sterile cotton swabs, pre-moistened in purified water.
In cases where pathogenic microorganisms affect the skin, smears are taken after skin treatment with an antiseptic. Previously, the wounds are cleaned of the formed crusts.
Medical treatment

Therapy for staphylococcal infections can be carried out at home without hospitalization in a medical facility. Inpatient treatment is indicated in cases where sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, or purulent-necrotic lesions are established.
First of all, an antibacterial agent is selected for patients based on the results of bacteriological culture. The preparations can be used in the form of tablets, injections.Since each strain of staph infection has its own characteristics and is sensitive to a particular drug, there is no single drug.
The following groups of drugs are often prescribed:
- penicillin series.
- Cephalosporins.
- Macrolides.
- Lincosamides.
When diagnosing a staphylococcal infection, the patient should adhere to all the rules and time of administration, dosage of the drug. The minimum course of therapy should be at least 5 days.
If you stop taking the drug immediately after the disappearance of symptoms, over time, pathogenic microorganisms will begin to spread again. In this case, it is necessary to conduct repeated tests and prescribe another remedy. This is due to the fact that bacteria will develop resistance to the agent used.In some cases, the doctor may extend the course of antibiotic treatment. But it is important to know that therapy should not be interrupted.
When establishing the presence of purulent lesions, ointments with a fatty base are not recommended, as they prevent the outflow of exudate.
Bacteriophages can be used to kill staphylococcal infections. These are special viruses that affect only staphylococcus aureus. They are contained in preparations for topical use. The composition of the ointments also includes antibiotics, they have an antiseptic and regenerating effect.
Folk recipes and methods of treatment

The use of folk methods and recipes can cause the development of consequences and various complications. That is why you should consult your doctor before using them.
Some of the most popular recipes for staphylococcal lesions are:
- Apricot. Effective for skin diseases. It activates the regeneration process, accelerates the healing process. To do this, apply the pulp of the fruit to the affected areas. With internal infections, you need to use apricot puree twice a day before meals.
- Garlic. Also used for skin lesions. To prepare the infusion, you need 50 grams of garlic and 150 ml of water. Chop the garlic, add water and mix. Insist for half an hour and strain. In the resulting solution, you need to moisten the bandage and apply to the affected areas of the skin. The duration of the procedure is 10 minutes, carried out twice a day. The course of therapy is 10 days.
- St. John's wort. Helps restore immunity and reduce inflammation. To prepare the infusion, pour 2 teaspoons of dry St. John's wort with a glass of boiling water. Cover the container with a clean cloth and insist for half an hour. Take before meals twice a day.
- Chamomile. It is a natural antiseptic and helps to relieve inflammation. On its basis, a healing decoction is made. Two teaspoons of a dry plant should be poured with a glass of water and boiled for five minutes. Strain the resulting solution and cool. It is used for wiping damaged areas of the skin and gargling.
- To strengthen the immune system, it is recommended to use blackcurrant. Berries contain large amounts of vitamin C.
Patients should remember that with a staphylococcal infection, thermal procedures are strictly prohibited, which are used to speed up the process of opening abscesses. An increase in temperature contributes to the activation of the reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, which leads to the development of complications. It is forbidden to visit baths, saunas, pools during the period of therapy.

Staphylococcal infection is difficult to cure, due to the ability of bacteria to survive in drought, high temperature or high humidity. But it is impossible to completely get rid of microorganisms, since they belong to the conditionally pathogenic flora of the body.
To prevent the reproduction and spread of microorganisms, a number of rules should be observed:
- Wash hands after going to the toilet, walking and before eating.
- Treat wounds with antiseptic agents.
- Prevent excessive sweating.
- Do not eat food with broken package integrity.
- Wash vegetables and fruits.
Staphylococcus is dangerous to humans, as it causes the development of serious complications. If symptoms of infection appear, you should contact a specialist and immediately begin treatment.
Bacteria are always found on the surface of the mucosa and skin. In minimal quantities, they are not capable of harming the human body. But under the influence of external or internal factors, microorganisms become a threat to health. Preventive measures must always be followed to prevent the spread of staphylococcus and damage to internal organs.

