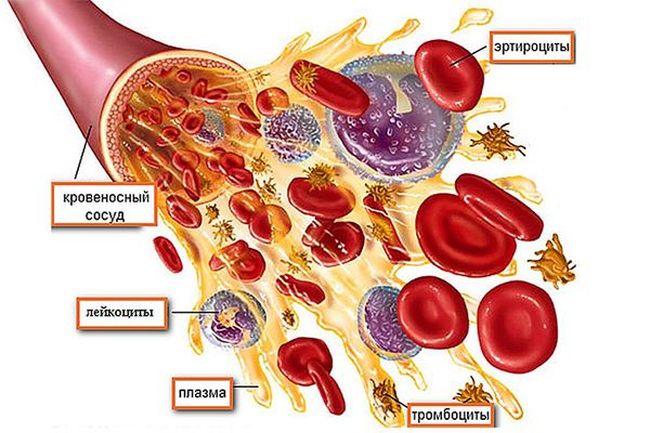
Red blood cells are one of the components of the blood, which is involved in blood circulation and the functioning of the body. They are formed in the bone marrow. If the red blood cells are elevated, then the patient has a certain pathology that can be detected only after the examination.
What are erythrocytes
Erythrocytes are red non-nuclear blood cells that perform the following functions:
- Transport. They move oxygen from the lungs to all tissues and organs and take the exhausted carbon dioxide back to the lungs. In addition, they carry amino acids, lipids and proteins.
- Regulation of blood acidity and participation in coagulation.
- Participation in water-salt metabolism.
- Protective. Red blood cells provide immune responses by strengthening the blood and tissue barriers against various infections.
- Homeostatic. Maintenance of body temperature, participation in tissue repair.
The composition of erythrocytes includes:
- hemoglobin - 95-96%;
- lipids and protein - 4-5%.
The duration of their life lasts no more than 4 months. RBCs die in the spleen. This process is a natural cell renewal.
The normal level of red blood cells in women is from 3.7 to 4.7 million per 1 µl. In men, the indicator is from 4 to 5.1 million in 1 µl.
Nuance! During pregnancy, a woman may have a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood to 3-3.5 million in 1 µl.
In children under 1 year old, the average volume of erythrocytes in the blood changes all the time, therefore, a special scheme has been developed for which the indicators for each month are prescribed (for newborns - for each day).
During adolescence in children, the level of red blood cells corresponds to the level of adults.
What is hemoglobin?
Hemoglobin is a complex component of erythrocytes, which includes a protein-globin and an iron-containing part-heme.
Hemoglobin in the blood performs the following functions:
- Active participation in the processes of gas exchange of the body with environmental factors.
- Movement of blood from the lungs to tissues and organs.
- Maintaining the acid-base balance in the body.
The reasons for the increase in hemoglobin levels include:
- Excessive amount of glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus.
- Erythrocytosis.
- Thickening of the lymph.
- Oncological diseases.
- Poor intestinal permeability.
- Violations in the activity of the cardiovascular system.
- An excess of B vitamins in the body.
Symptoms of elevated hemoglobin are:
- pale skin;
- blurred vision;
- poor appetite;
- constant sleepiness;

- loss of working capacity;
- dysfunction in the activity of the genitourinary system.
To lower hemoglobin, red berries and fruits, organ meats and cereals should be excluded from the diet. It is also forbidden to use butter, smoked meats and sweets.
- fish;
- salads;
- poultry meat;
- legumes;
- salads.
To lower the hemoglobin content, doctors prescribe special medications. The most common are Aspirin, Cardiomagnyl and Trental.
Beneficial for patients are outdoor walks and moderate exercise.
Causes of elevated red blood cells in adults
An increased level of red cells in the blood is called erythrocytosis. This phenomenon is rare and often the reasons for the physiological increase in the number of red blood cells in the lymph are:
- Frequent stress and emotional overstrain.
- Excessive dehydration of the body.
- Strong physical activity.
The following diseases can provoke an increase in red blood cells:
- erythremia;
- heart defects;
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- pathology of the respiratory tract;
- Aerza's disease.
Less dangerous causes of an increased erythrocyte count in the blood are the following processes:
- Smoking leading to an excess of carboxyhemoglobin.
- Deficiency of vitamins and minerals as a result of improper functioning of the liver.
- Lack of enzymes important for digestion, as a result of which the body is forced to produce red blood cells to digest food.
- Drinking poor quality water.
Only a qualified specialist can identify elevated red blood cells in the blood and explain to the patient what this means. He will treat the patient, focusing on the cause of the increase in blood cells.
Why is the red blood cell count high in a child?
If a blood test revealed elevated red blood cells in the blood of a child, then this may be a sign of such pathologies:
- Violation of the functioning of the bone marrow.
- Blood diseases.
- Respiratory diseases.
- Obesity III or IV degree.
- Dehydration as a result of severe poisoning of the body.
- Violation of the activity of the adrenal cortex.
- Oncological diseases of the liver.
The following factors can influence the increase in the level of red blood cells:
- intense physical activity;
- place of residence;
- dehydration due to increased sweating;
- second hand smoke.
Favorable is the place of residence, which is lower above sea level.
Symptoms of an increased number of red blood cells
For a high rate of red blood cells in the blood, the following symptoms are characteristic:
- strong;

- dizziness and fainting;
- breaking in the bones;
- decreased vision and hearing;
- unstable emotional state;
- nosebleeds;
- obstruction of the outflow of blood.
Patients with erythrocytosis have viscous and thick blood that does not flow well. This is noticeable on examination.
When is a blood test for red blood cells needed?
There is no separate analysis for red blood cells; it is included in the general blood test. It is prescribed in such cases:
- Monitoring the condition of a pregnant woman.
- Prevention.
- Diagnosis of anemia.
- If you suspect a pathology of the hematopoietic system.
- Control over current treatment.
Such an analysis is designated in the form of a blood test in the form of the letters RBC. If the specialist does not have enough information on this analysis, he prescribes a blood test with the addition “with ESR”. It is more detailed and costs patients more. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate can be analyzed separately.
How is the blood sampling procedure carried out?
There is no need for any preparatory measures for donating blood. The last meal should be 5 hours before the analysis. It is advisable to refrain from strong physical and emotional stress on the eve of the study, and also not to drink alcohol. Before entering the office, it is better to rest for 10 minutes.
Treatment
The course of therapy for erythrocytosis is aimed at eliminating excess red blood cells by reducing the level of lymph viscosity. Treatment consists in the use of drugs. Doctors prescribe them in accordance with the individual characteristics of the patient. If erythrocytosis is caused by diseases of the respiratory system, then the underlying pathology is treated first, which provoked an increase in red blood cells. Vascular shunts are treated with surgery.
Patients with hypoxic forms will require oxygen therapy. It is used to treat acute and chronic respiratory failure. It has the best effect if the patient lives in high mountains. The worst result therapy brings with anemia. With congenital defects of the septa of the hearts, this method of treatment is inappropriate. Oxygen therapy is used to improve the functioning of the liver and kidneys.
In infectious pathology, treatment is aimed at eliminating the pathogen.
One of the modern methods of treatment is bloodletting. It requires caution in chronic lung pathologies and heart defects. After the procedures, the patient is administered glucose, plasma and isotonic sodium chloride solution. The method of bloodletting is used to treat newborns.
Adolescent children may be prescribed hirudotherapy instead of bloodletting therapy. For this, medical leeches are used. In some cases, oxygen therapy is prescribed. Its essence lies in the fact that the patient inhales air enriched with oxygen. To avoid the effect of dryness, the air is humidified.
If a child has an elevated level of erythrocytes, then the specialist prescribes erythrocytepheresis. During treatment, the doctor takes a blood sample, then places it in a separator, which extracts the red blood cells. The remaining components are administered back to the patient. To achieve a positive result, 2 courses of therapy are required.
When diagnosing an advanced form of erythrocytosis, the doctor prescribes drugs that help thin the blood. They lead to the normalization of blood clotting and prevent the formation of blood clots.
To avoid excessive thickening of the blood, you should drink as much liquid as possible. It can be not only water, but also teas, juices, compotes and herbal infusions.

